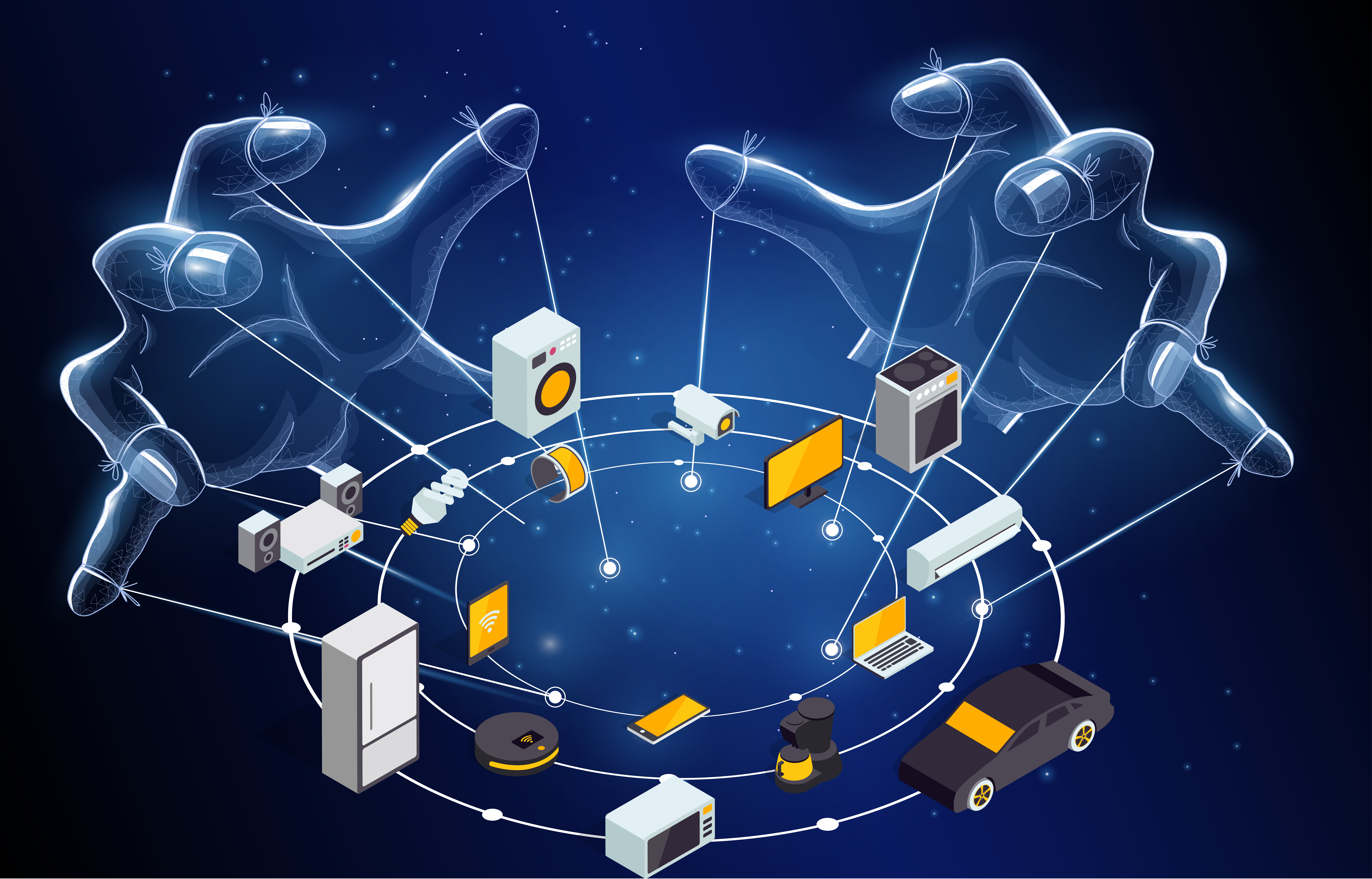
Internet of things (IoT) has been defined as a global infrastructure for the information society, enabling advanced services by interconnecting
Internet of Things?
Internet of things (IoT) has been defined as a global infrastructure for the information society, enabling advanced services by interconnecting (physical and virtual) devices and equipment based on the Internet. All devices can communicate with each other anytime, anywhere over the Internet.
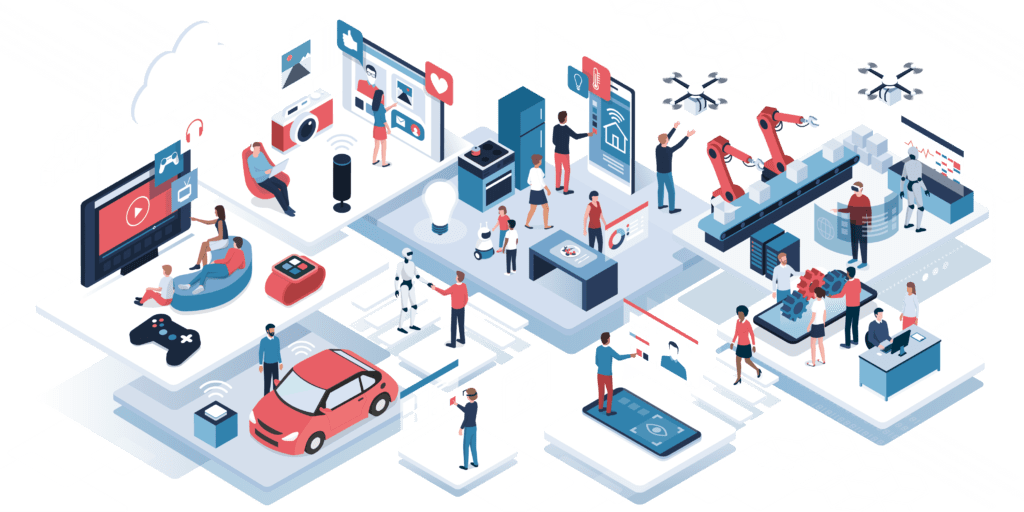
The wide application of IoT includes smart healthcare, smart home, smart living, environmental monitoring, energy management, intelligent transport system, etc.
In our daily lives, IoT devices include everything from routers, smart TVs, smart light bulbs, webcams, smart door locks, smart air-conditioners to our personal devices including laptops, smart phones, smart watches and handheld game consoles.
These smart devices collect data from the environment around them, such as location, time, temperature, brightness, humidity, heart rate or appearance. They are connected to the Internet through telecommunications network (e.g. 4G or 5G mobile network) and by intelligent processing and analysis of big data, they can perform their smart functions on devices and appliances.







Why is the risk of IoT increasing?
In 2021, the number of IoT devices amounted to 14 billion globally. It is predicted that the number will significantly increase to 31 billion in 2025. While the IoT devices are gaining popularity, they have posed critical cyber security threats. IoT devices are more vulnerable to cyber attacks than mobile phones or computers, the reasons include:
- The functions of IoT devices varies. Different IoT devices require tailor-made operating systems. The design of these systems is often simple. The producers will not provide regular updates of their systems for cost-saving. There is also a lack of available security software or antivirus software to protect IoT devices in the market.
- Some IoT devices do not have strict factory security settings, while some enable unnecessary network service functions (e.g. File Transfer Protocol and Remote Desktop Protocol, etc.), which are exposed to high cyber security risks.
- Many users have insufficient awareness of IoT security. They often use default passwords or simple passwords for convenience purposes, leaving loopholes for hackers.
A report from a cyber security company revealed that, more than 1 billion IoT attacks took place in 2021, nearly 900 million of which were IoT-related phishing attacks.
Consequences of compromised IoT devices
Once a hacker intruded into one of your smart home devices, he/she may also gain access to other devices in the same network (e.g. router, personal computer, mobile phone, digital door lock) and even obtain the access control. Imagine that if a hacker intrudes into your IP cameras and learns that you are out for work, and clandestinely unlocks your digital door lock, your home will then be exposed to the risk of burglaries. If a hacker intrudes into an electric vehicle with automatic navigation connected to the Internet and interferes its driving automation, it may cause serious consequences.
Apart from property or privacy threats, your devices may become a member of the “Botnet” and an accomplice without knowledge in attacking other computers. In 2021, hackers initiated the largest scale on record DDoS attacks (up to 17.2 million request per second) to Cloudflare. It is reported that the hackers launched attacks to Cloudflare’s server using over 20,000 Mirai-infected IoT devices. It can be seen that a “Botnet” formed by IoT devices may cause tremendous destruction.
The report noted that the most vulnerable IoT devices are as follow:
- Routers 46%
- Access Points 17%
- Extenders & Mesh 17%
- NAS 5 %
- VoIP 4%
- Cameras 3%
- Smart Home Devices 3%
Routers were attacked most often for one simple reason – the vast majority of homes and businesses have at least one. Routers are the nexus of all communication between IoT devices and, as such, are the most vulnerable
part of the network.
Security tips on IoT
- Before use for the first time, change the default password to a strong one. It is more secure to adopt multi-factor authentication if available.
- Disable unnecessary functions, such as FTP, TELNET, etc.
- Enable activity records and check from time to time if there is any suspicious activity.
- Enable firewall and network monitoring if possible, and update firmware regularly.
- Use encrypted transmission when controlling IoT devices remotely.
You may be interested in
Artificial Intelligence (AI in abbreviation) is a technique of machine imitating human intelligence. In the 50’s, there were scientists suggesting…
The Hong Kong Monetary Authority (HKMA) unveiled “Fintech 2025” in the mid-2021, which aims to encourage the financial sector to…
The Internet reaches almost everywhere and contains massive source of information. How much information is accessible to the public? From…
In the digital age, teenagers have started to use the Internet since their childhood. Online content varies greatly. To what…
Some members of public might raise suspicion when receiving SMS messages from the government departments with a prefix +852 in…
Welcome to the metaverse journeyThe concept of the Metaverse originates from Snow Crash, a science fiction novel published in 1992…