
Phishing attack is a prevalent cybercrime which can take various forms.
What is phishing attack?
Phishing attack is a prevalent cybercrime. Hackers send phishing emails or text messages impersonating organisations such as the government, banks, online payment service providers, online retailers or business partners, with links or QR codes directing to phishing websites which look like the genuine websites of relevant organisations, tricking the recipients into inputting login passwords, personal information, credit card details, etc. Hackers may also attach links, QR codes or files in the messages, if the recipients click on the links or open attachments indiscriminately, their devices may be infected by malware.
Phishing emails and text messages
Phishing Website
What are the latest hacking tricks?
Among the phishing cases last year, most hackers were impersonating financial institutions and post offices to send out phishing emails or text messages.
Impersonating financial institutions/ e-payment platforms
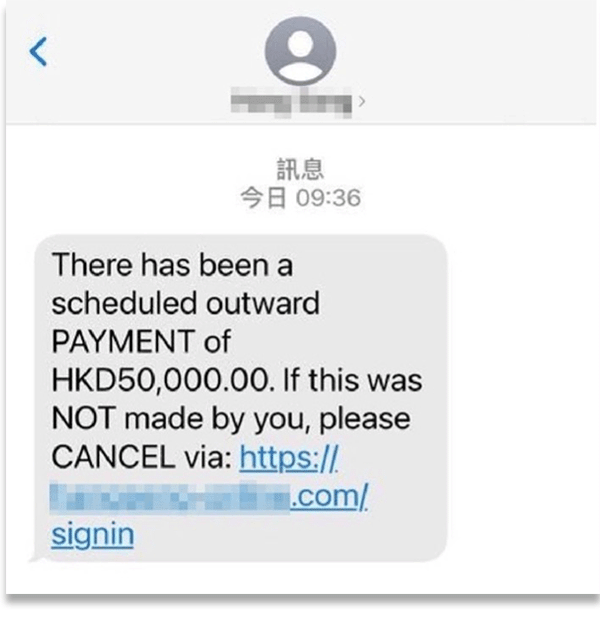
Hackers impersonate financial institutions, such as banks, and send phishing text messages to the victims, claiming irregularities detected or updates on the payment instructions, and request users to process or confirm. They lured the victims into visiting a fraudulent website and providing their mobile numbers and one-time-password. The hackers then hijack the accounts by using another mobile and transfer funds out. As the scammers hide the senders’ mobile numbers and pretend to send messages under bank names, mobile systems will treat those messages as no difference with those under the same bank names. Users are confused by the mixed genuine and fake messages.
There are also some hackers who gather personal information via various channels (e.g. system loophole, dark web), then impersonate bank staff to make calls and request the users to provide “PIN” and “one-time-password” to update their e-payment accounts, otherwise their accounts will be frozen. As scammers are able to state the personal information of the call recipients, they are easily trusted by the victims. After getting the above information, the scammers will then hijack the accounts and drain their deposits.
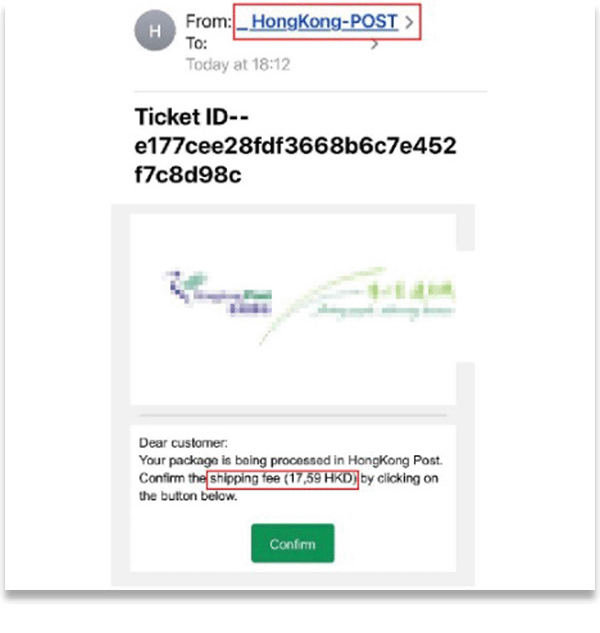
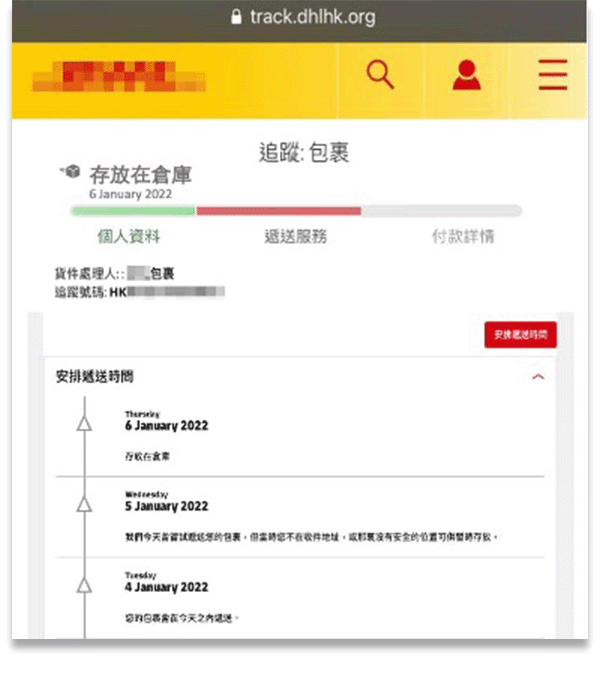
Impersonating postage services/ public institutions
“Delivery failure, incomplete information”, “Payment failure, please confirm”, “Your package with track number xxxx still waiting your instruction” are examples of phishing messages purporting to be sent from public institutions such as the post office, electricity company, gas company, MTR. Victims are lured into clicking on the embedded links which take them to fraudulent websites. With the phishing message interfaces look almost the same as the authentic ones and by using some imminent wording like “service suspended”, “return of parcel”, the recipients often provide personal or credit card information out of anxiety.
Pay attention to the email header of the sender. Check if there is anything unusual regarding the domain of the email address.
The subject includes wording “the account will soon be suspended”, exploiting recipients’ anxiety to lower their guard.
The email content is inconsistent, with grammatical or spelling mistakes.
The email contains suspicious links, QR codes or attachments.
The domain of the fraudulent website looks very much like that of the official website (e.g. the number “1” is replaced with the letter “ I”)
Some of the links on the fraudulent websites may be broken.
Security tips

Do not open unknown emails or messages

Check the sender’s details carefully

Do not click on the hyperlinks in suspicious emails or messages

Do not log into websites that are not verified

Pay extra attention if the websites ask for personal or credit card details

If you suspect that you have fallen prey to a scam, save relevant emails or messages and report the case to the police.
You may be interested in
Fraudsters steal information through the Internet such as names Identity Theft Fraudsters steal information through the Internet such as names,…
refers to an attack in which. attacker monitors the communication between the sender and What is Man-in-the-middle Attack? A man-in-the-middle…
An APT is a common cyberattack which is meticulously planned against specific What is an APT attack? An APT is…
The Internet of Things is a system of mobile devices or household equipment What is Internet of Things (IoT)? The…
Hackers utilise multiple infected computer systems (i.e. Botnet) to generate huge volumes of traffic, overloading the What is Distributed Denial…
Ransomware is a malware that prevents or restricts users from accessing computer systems. Hackers will What is Ransomware? Ransomware is…

